more than you ever wanted to know about...
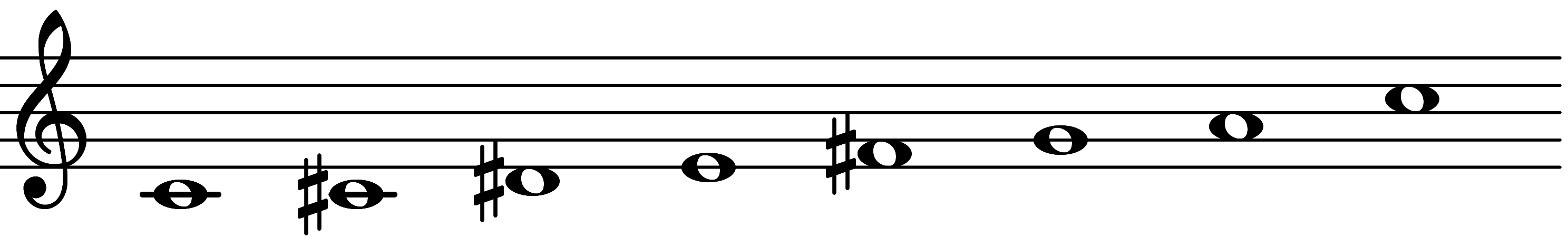
Scale 731: "Alternating Heptamode"

Bracelet Diagram
Tonnetz Diagram
Keyboard Diagram
Other diagrams coming soon!
Common Names
Names are messy, inconsistent, polysemic, and non-bijective. If you see a name with lots of citations beside it, that's a good measure of credulity.
Unsorted
- 1MA & 3∅7[0]
- 1◦7 & 2◦[0]
- 1◦ & 67[0]
Western Altered
- Alt 67[1][2]
- Superlocrian 67[6]
- Ultralocrian 7[7]
Western Modern
- Alternating Heptamode
Dozenal
- EMOian[3]
Western
- Hungarian Major Mode II[4]
Zeitler
- Ionorian[5]
Name Sources
- [0] Ring, Ian: The Exciting Universe Of Music Theory retrieved 2024-11-26
- [1] Carl, Jeffrey: Strings And Ivory: The Exhaustive Book of Scales & Modes. 2020
- [2] Bedwell, Robert: Modal Method of Music. 2023. Locrian Publishing, Brighton, East Sussex.
- [3] Pecot, Justin: The Dozenal Standard, 2nd editon. Available from justinpecot.com.
- [4] Rechberger, Herman: Scales and Mode Around the World. ISBN: 978-952-5489-07-1. Preview with Google Books
- [5] Zeitler, William: "all the scales". https://allthescales.org. Retrieved April 2024
- [6] Balena, Francesco: Scale Omnibus. version2.02 (2022) midi2themax.com. Amazon
- [7] Cochrane, Rich: Arpeggio and Scale Resources, a Guitar Encyclopedia. Big Noise Publishing, London UK.
Analysis
CardinalityCardinality is the count of how many pitches are in the scale. Cardinalities can be expressed as an adjective, e.g. pentatonic, hexatonic, heptatonic, and so on. |
7 (heptatonic) |
Pitch Class SetThe tones in this scale, expressed as numbers from 0 to 11. |
{0,1,3,4,6,7,9} |
Leonard NotationAs practiced in the theoretical work of B P Leonard, this notation for describing a pitch class set replaces commas with subscripted numbers indicating the interval distance between adjacent tones. Convenient when you are doing certain kinds of analysis. The superscript in parentheses is the sonority's Brightness. | [01123142617293](30) |
Rotational SymmetrySome scales have rotational symmetry, sometimes known as "limited transposition". If there are any rotational symmetries, these are the intervals of periodicity. |
none |
Reflection AxesIf a scale has an axis of reflective symmetry, then it can transform into itself by inversion. It also implies that the scale has Ridge Tones. Notably an axis of reflection can occur directly on a tone or half way between two tones. |
none |
PalindromicityA palindromic scale has the same pattern of intervals both ascending and descending. |
no |
ChiralityA chiral scale can not be transformed into its inverse by rotation. If a scale is chiral, then it has an enantiomorph. |
yes enantiomorph: 2921 |
HemitoniaA hemitone is two tones separated by a semitone interval. Hemitonia describes how many such hemitones exist. |
3 (trihemitonic) |
CohemitoniaA cohemitone is an instance of two adjacent hemitones. Cohemitonia describes how many such cohemitones exist. |
0 (ancohemitonic) |
ImperfectionsAn imperfection is a tone which does not have a perfect fifth above it in the scale. This value is the quantity of imperfections in this scale. |
4 |
ModesModes are the rotational transformations of this scale. This number includes the scale itself, so the number is usually the same as its cardinality; unless there are rotational symmetries then there are fewer modes. |
7 |
Prime FormDescribes if this scale is in prime form, using the Starr/Rahn algorithm. |
yes |
Forte ClassA code assigned by theorist Allen Forte for this pitch class set and all of its transpositional (rotation) and inversional (reflection) transformations. |
7-31 |
GeneratorIndicates if the scale can be constructed using a generator, and an origin. |
none |
Deep ScaleA deep scale is one where the interval vector has 6 different digits, an indicator of maximum hierarchization. |
no |
Interval StructureDefines the scale as the sequence of intervals between one tone and the next. |
[1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 3] |
Interval VectorDescribes the intervallic content of the scale, read from left to right as the number of occurences of each interval size from semitone, up to six semitones. |
<3, 3, 6, 3, 3, 3> |
Hanson's Interval SpectrumThe same as the Interval Vector, but expressed in a syntax used by Howard Hanson. Hanson categorizes all intervals as being one of six classes, and gives each a letter: p m n s d t, ordered from most consonant (p) to most dissonant (t). When an interval appears more than once in a sonority, it is superscripted with a number, like p2. |
p3m3n6s3d3t3 |
Proportional Saturation VectorFirst described by Michael Buchler (2001), this is a vector showing the prominence of intervals relative to the maximum and minimum possible for the scale's cardinality. A saturation of 0 means the interval is present minimally, a saturation of 1 means it is the maximum possible. | <0.25, 0.25, 1, 0, 0.25, 1> |
Distribution SpectraDescribes the specific interval sizes that exist for each generic interval size. Each generic <g> has a spectrum {n,...}. The Spectrum Width is the difference between the highest and lowest values in each spectrum. |
<1> = {1,2,3} <2> = {3,4,5} <3> = {4,5,6} <4> = {6,7,8} <5> = {7,8,9} <6> = {9,10,11} |
Spectra VariationDetermined by the Distribution Spectra; this is the sum of all spectrum widths divided by the scale cardinality. |
1.714 |
Maximally EvenA scale is maximally even if the tones are optimally spaced apart from each other. |
no |
Maximal Area SetA scale is a maximal area set if a polygon described by vertices dodecimetrically placed around a circle produces the maximal interior area for scales of the same cardinality. All maximally even sets have maximal area, but not all maximal area sets are maximally even. |
no |
Interior AreaArea of the polygon described by vertices placed for each tone of the scale dodecimetrically around a unit circle, ie a circle with radius of 1. |
2.549 |
Polygon PerimeterPerimeter of the polygon described by vertices placed for each tone of the scale dodecimetrically around a unit circle. |
5.967 |
Myhill's PropertyA scale has Myhill's Property if the Distribution Spectra have exactly two specific intervals for every generic interval. |
no |
Centre of Gravity DistanceWhen tones of a scale are imagined as physical objects of equal weight arranged around a unit circle, this is the distance from the center of the circle to the center of gravity for all the tones. A perfectly balanced scale has a CoG distance of zero. |
0.142857 |
Ridge TonesRidge Tones are those that appear in all transpositions of a scale upon the members of that scale. Ridge Tones correspond directly with axes of reflective symmetry. |
none |
ProprietyAlso known as Rothenberg Propriety, named after its inventor. Propriety describes whether every specific interval is uniquely mapped to a generic interval. A scale is either "Proper", "Strictly Proper", or "Improper". | Improper |
Heteromorphic ProfileDefined by Norman Carey (2002), the heteromorphic profile is an ordered triple of (c, a, d) where c is the number of contradictions, a is the number of ambiguities, and d is the number of differences. When c is zero, the scale is Proper. When a is also zero, the scale is Strictly Proper. | (4, 27, 84) |
Coherence QuotientThe Coherence Quotient is a score between 0 and 1, indicating the proportion of coherence failures (ambiguity or contradiction) in the scale, against the maximum possible for a cardinality. A high coherence quotient indicates a less complex scale, whereas a quotient of 0 indicates a maximally complex scale. | 0.779 |
Sameness QuotientThe Sameness Quotient is a score between 0 and 1, indicating the proportion of differences in the heteromorphic profile, against the maximum possible for a cardinality. A higher quotient indicates a less complex scale, whereas a quotient of 0 indicates a scale with maximum complexity. | 0.333 |
BrightnessBased on the theories of B P Leonard, Brightness is a measurement of interval content calculated by taking the sum of each tone's distance from the root. Scales with more tones at higher pitches will have a greater Brightness than those with fewer, lower pitches. Typically used to compare pitch class sets with the same cardinality. | 30 |
XenomeA naming schema invented by Qid Love, and published in their book The Book Of Xenomes. A xenome is a succinct encoding of the pitch class set as three hexadecimal characters, with reversed bits such that they read left to right as ascending pitches. |
DB4 |
Lewin-Quinn FC ComponentsConceived by David Lewin in 1959, and generalized by Ian Quinn; FC is a function that transforms the set by multiplying by a given number of semitones, then gives the total distance of the sum of the vectors produced by each tone when mapped to a circular plane. The result is a discrete Fourier transform that quantifies harmonic qualities. A more thorough and sensible explanation is coming in the book. FC Components can be used to analyze other tuning systems besides 12-TET. FC0 is the cardinality of the scale. |
FC0 = 7 FC1 = 1 FC2 = 1 FC3 = 1 FC4 = 3.605551 FC5 = 1 FC6 = 1 |
Tertian Harmonic Chords
Tertian chords are made from alternating members of the scale, ie built from "stacked thirds". Not all scales lend themselves well to tertian harmony.
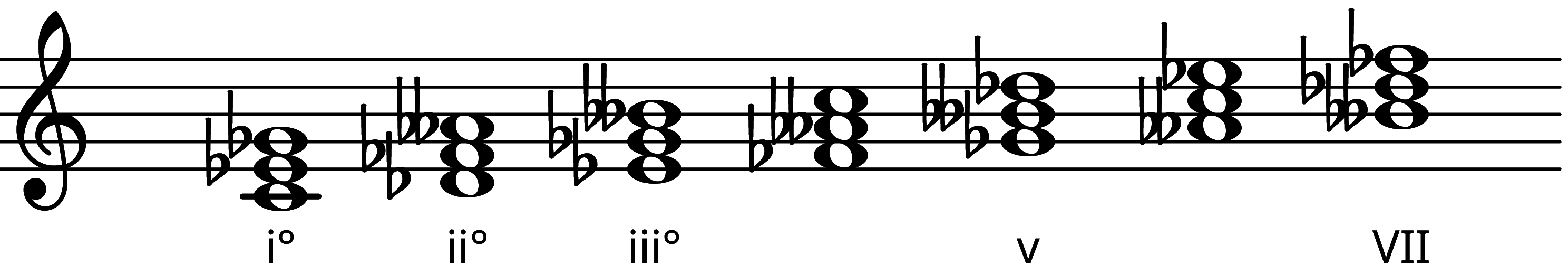

Generator
This scale has no generator.
Common Triads
These are the common triads (major, minor, augmented and diminished) that you can create from members of this scale.
* Pitches are shown with C as the root
| Triad Type | Triad* | Pitch Classes | Degree | Eccentricity | Closeness Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major Triads | C | {0,4,7} | 3 | 3 | 1.7 |
| A | {9,1,4} | 3 | 3 | 1.7 | |
| Minor Triads | cm | {0,3,7} | 3 | 3 | 1.8 |
| f♯m | {6,9,1} | 3 | 3 | 1.8 | |
| am | {9,0,4} | 4 | 3 | 1.6 | |
| Diminished Triads | c° | {0,3,6} | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| c♯° | {1,4,7} | 2 | 3 | 2 | |
| d♯° | {3,6,9} | 2 | 3 | 2 | |
| f♯° | {6,9,0} | 2 | 3 | 1.9 | |
| a° | {9,0,3} | 2 | 3 | 1.9 |
Above is a graph showing opportunities for parsimonious voice leading between triads*. Each line connects two triads that have two common tones, while the third tone changes by one generic scale step.
| Diameter | 3 |
|---|---|
| Radius | 3 |
| Self-Centered | yes |
Modes
Modes are the rotational transformation of this scale. Scale 731 can be rotated to make 6 other scales. The 1st mode is itself.
| 2nd mode: Scale 2413 | 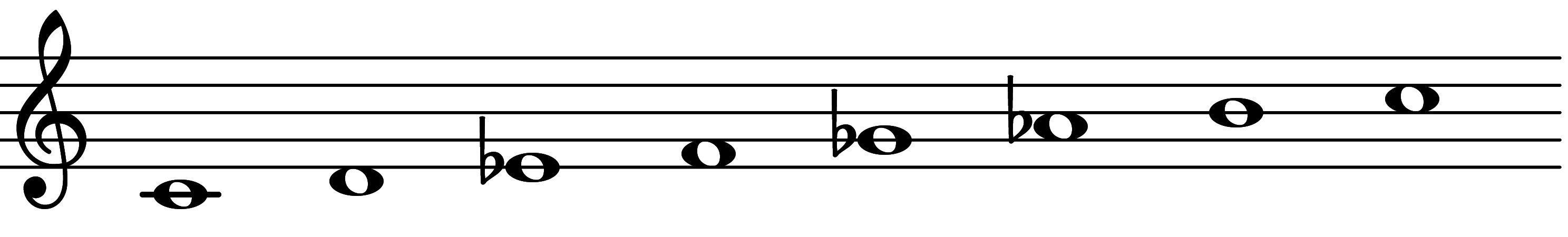 | Harmonic Minor 5 | |||
| 3rd mode: Scale 1627 | 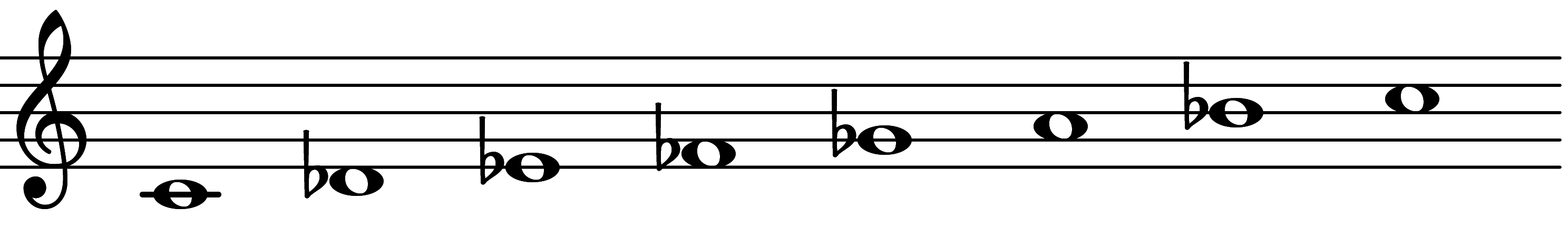 | Superlocrian 6 | |||
| 4th mode: Scale 2861 |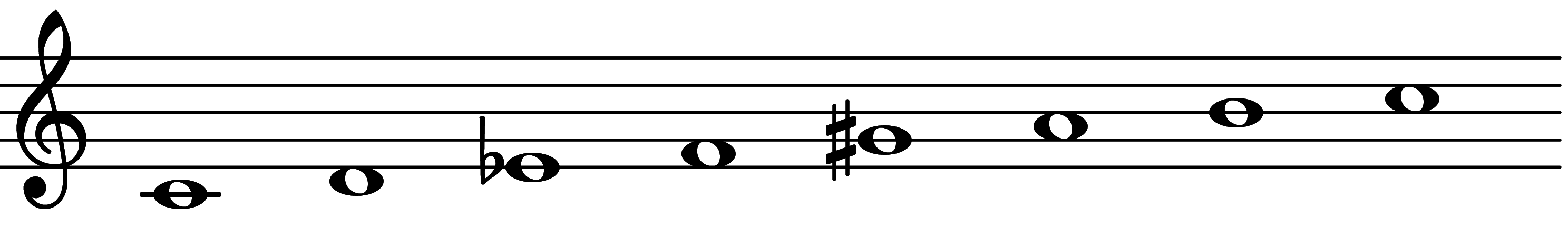  | Melodic + | |||
| 5th mode: Scale 1739 | 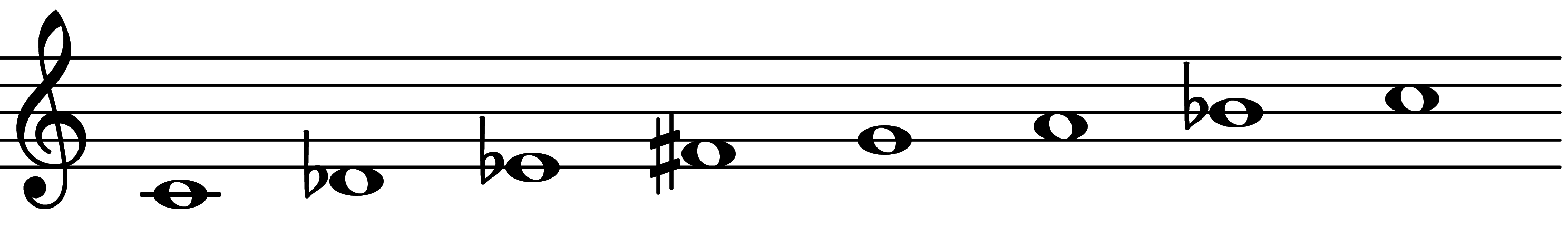 | Rāga Sthavarajam | |||
| 6th mode: Scale 2917 | 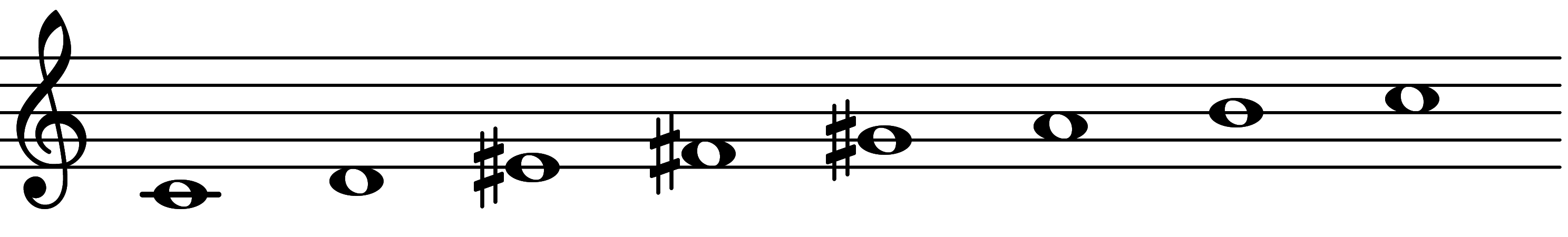 | Lydian Augmented 3 | |||
| 7th mode: Scale 1753 | 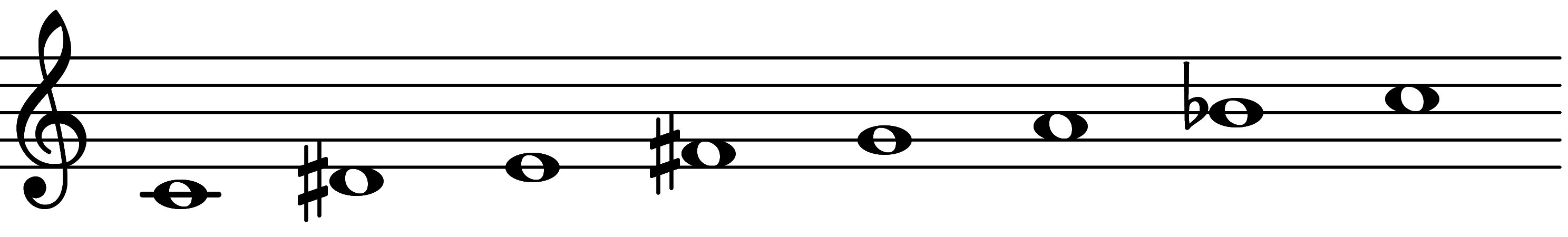 | Hungarian Major |
Prime
This is the prime form of this scale.
Complement
The heptatonic modal family [731, 2413, 1627, 2861, 1739, 2917, 1753] (Forte: 7-31) is the complement of the pentatonic modal family [587, 601, 713, 1609, 2341] (Forte: 5-31)
Inverse
The inverse of a scale is a reflection using the root as its axis. The inverse of 731 is 2921
| Scale 2921 | 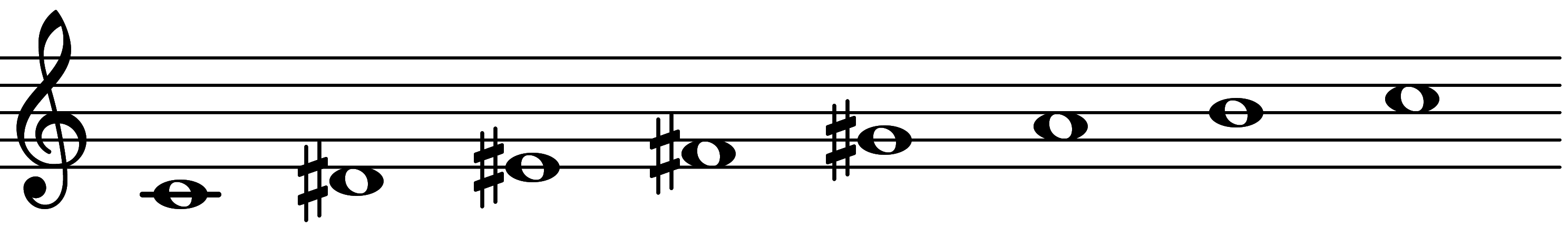 | Lydian Augmented 23 |
Interval Matrix
Each row is a generic interval, cells contain the specific size of each generic. Useful for identifying contradictions and ambiguities.
Contradictions (4) | Ambiguities(27) |
Hierarchizability
Based on the work of Niels Verosky, hierarchizability is the measure of repeated patterns with "place-finding" remainder bits, applied recursively to the binary representation of a scale. For a full explanation, read Niels' paper, Hierarchizability as a Predictor of Scale Candidacy. The variable k is the maximum number of remainders allowed at each level of recursion, for them to count as an increment of hierarchizability. A high hierarchizability score is a good indicator of scale candidacy, ie a measure of usefulness for producing pleasing music. There is a strong correlation between scales with maximal hierarchizability and scales that are in popular use in a variety of world musical traditions.
| k | Hierarchizability | Breakdown Pattern | Diagram |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 110110110100 | |
| 2 | 3 | 1([01]1[01])0([01]1[01]) | |
| 3 | 3 | 1([01]1[01])0([01]1[01]) | |
| 4 | 3 | 1([01]1[01])0([01]1[01]) | |
| 5 | 3 | 1([01]1[01])0([01]1[01]) |
Enantiomorph
Only scales that are chiral will have an enantiomorph. Scale 731 is chiral, and its enantiomorph is scale 2921
| Scale 2921 | 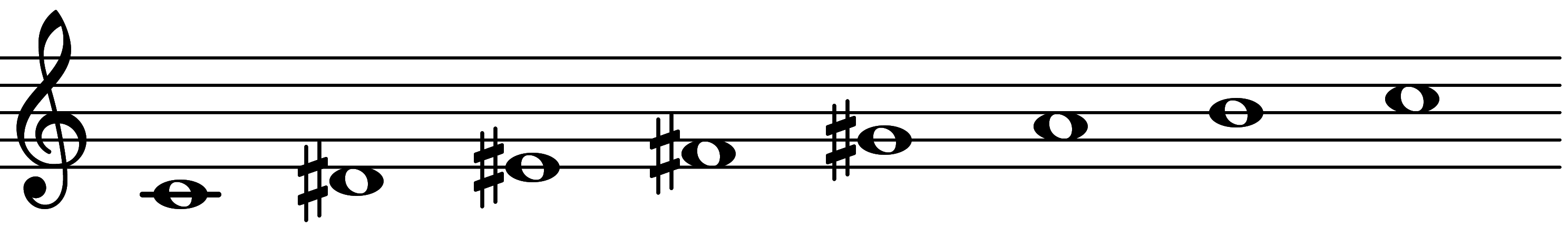 | Lydian Augmented 23 |
Center of Gravity
If tones of the scale are imagined as identical physical objects spaced around a unit circle, the center of gravity is the point where the scale is balanced.
| Position with origin in the center | (0.123718, 0.071429) |
|---|---|
| Distance from Center | 0.142857 |
| Angle in degrees measured clockwise starting from the root. | 120 |
| Angle in cents 100 cents = 1 semitone. | 400 |
Transformations:
In the abbreviation, the subscript number after "T" is the number of semitones of tranposition, "M" means the pitch class is multiplied by 5, and "I" means the result is inverted. Operation is an identical way to express the same thing; the syntax is <a,b> where each tone of the set x is transformed by the equation y = ax + b. A note about the multipliers: multiplying by 1 changes nothing, multiplying by 11 produces the same result as inversion. 5 is the only non-degenerate multiplier, with the multiplier 7 producing the inverse of 5.
| Abbrev | Operation | Result | Abbrev | Operation | Result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | <1,0> | 731 | T0I | <11,0> | 2921 | |||
| T1 | <1,1> | 1462 | T1I | <11,1> | 1747 | |||
| T2 | <1,2> | 2924 | T2I | <11,2> | 3494 | |||
| T3 | <1,3> | 1753 | T3I | <11,3> | 2893 | |||
| T4 | <1,4> | 3506 | T4I | <11,4> | 1691 | |||
| T5 | <1,5> | 2917 | T5I | <11,5> | 3382 | |||
| T6 | <1,6> | 1739 | T6I | <11,6> | 2669 | |||
| T7 | <1,7> | 3478 | T7I | <11,7> | 1243 | |||
| T8 | <1,8> | 2861 | T8I | <11,8> | 2486 | |||
| T9 | <1,9> | 1627 | T9I | <11,9> | 877 | |||
| T10 | <1,10> | 3254 | T10I | <11,10> | 1754 | |||
| T11 | <1,11> | 2413 | T11I | <11,11> | 3508 | |||
| Abbrev | Operation | Result | Abbrev | Operation | Result | |||
| T0M | <5,0> | 2921 | T0MI | <7,0> | 731 | |||
| T1M | <5,1> | 1747 | T1MI | <7,1> | 1462 | |||
| T2M | <5,2> | 3494 | T2MI | <7,2> | 2924 | |||
| T3M | <5,3> | 2893 | T3MI | <7,3> | 1753 | |||
| T4M | <5,4> | 1691 | T4MI | <7,4> | 3506 | |||
| T5M | <5,5> | 3382 | T5MI | <7,5> | 2917 | |||
| T6M | <5,6> | 2669 | T6MI | <7,6> | 1739 | |||
| T7M | <5,7> | 1243 | T7MI | <7,7> | 3478 | |||
| T8M | <5,8> | 2486 | T8MI | <7,8> | 2861 | |||
| T9M | <5,9> | 877 | T9MI | <7,9> | 1627 | |||
| T10M | <5,10> | 1754 | T10MI | <7,10> | 3254 | |||
| T11M | <5,11> | 3508 | T11MI | <7,11> | 2413 | |||
The transformations that map this set to itself are: T0, T0MI
Nearby Scales:
These are other scales that are similar to this one, created by adding a tone, removing a tone, or moving one note up or down a semitone.
| Scale 729 | 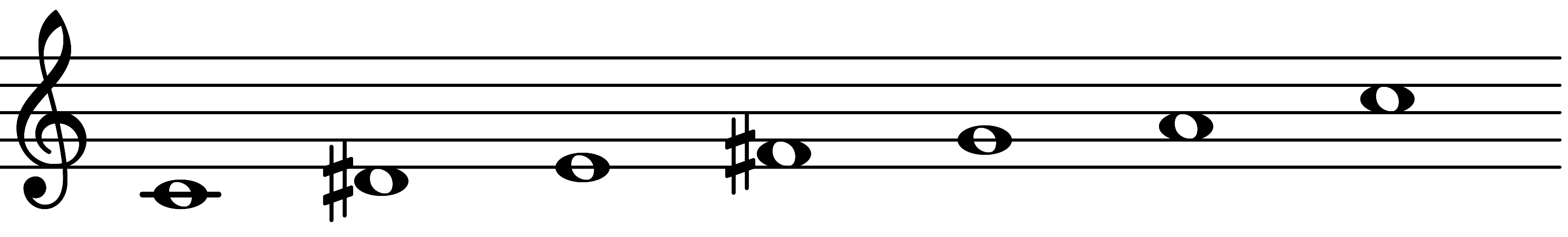 | 1MA & 3◦ | ||
| Scale 733 |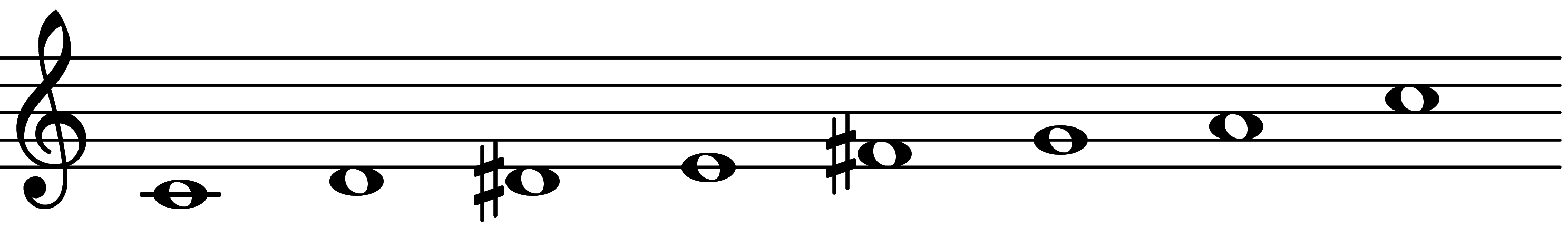  | Superlocrian 267 | ||
| Scale 735 | 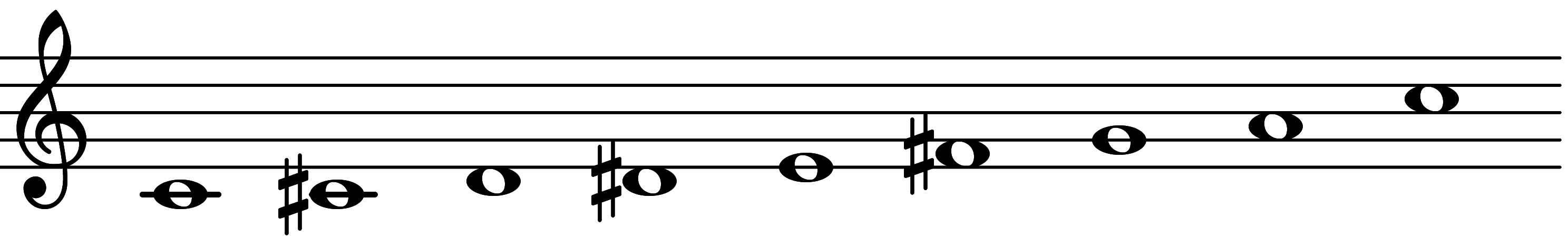 | African-American Blues II | ||
| Scale 723 | 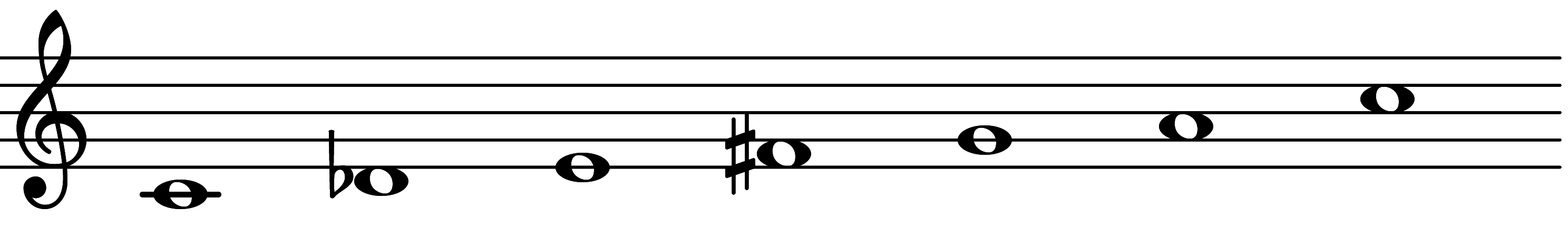 | Rāga Malavi | ||
| Scale 727 |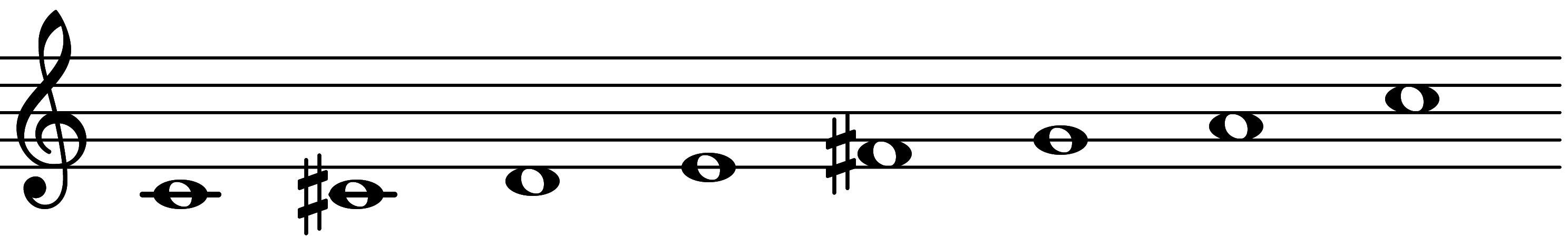  | Triadic Heptatonic 29 | ||
| Scale 715 | 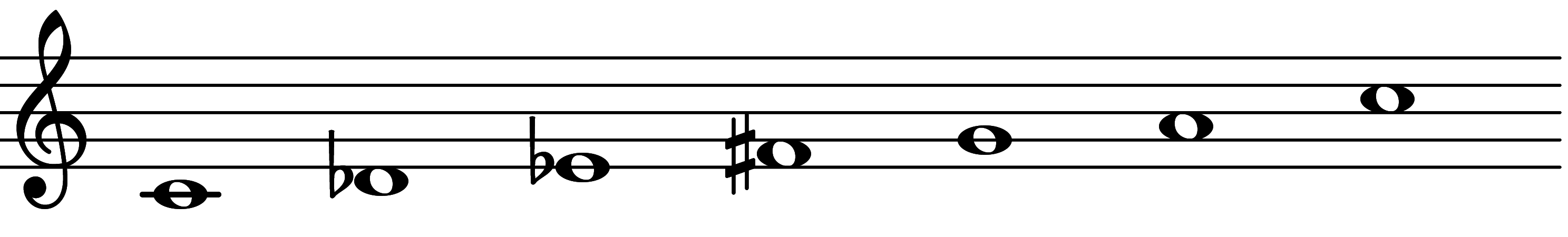 | T4 Prime Mode | ||
| Scale 747 | 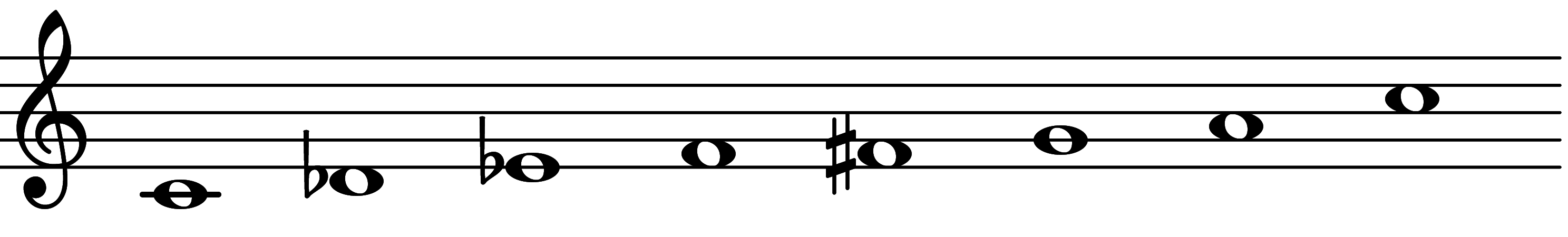 | 1SUS4 & 3∅7 | ||
| Scale 763 | 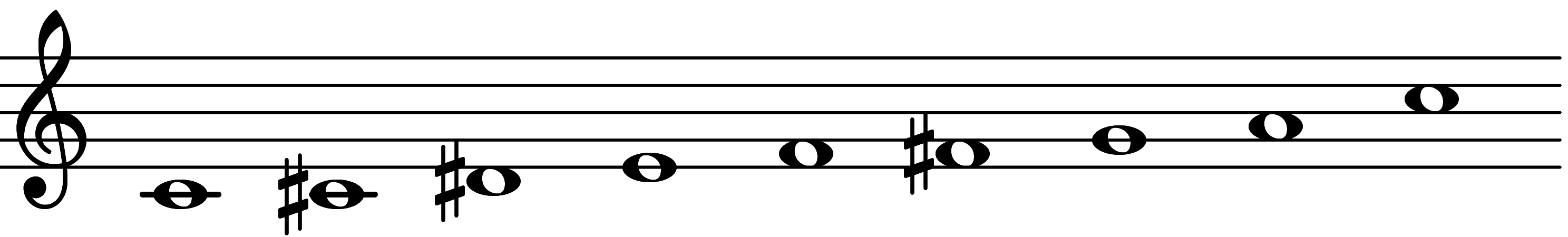 | Doryllic | ||
| Scale 667 | 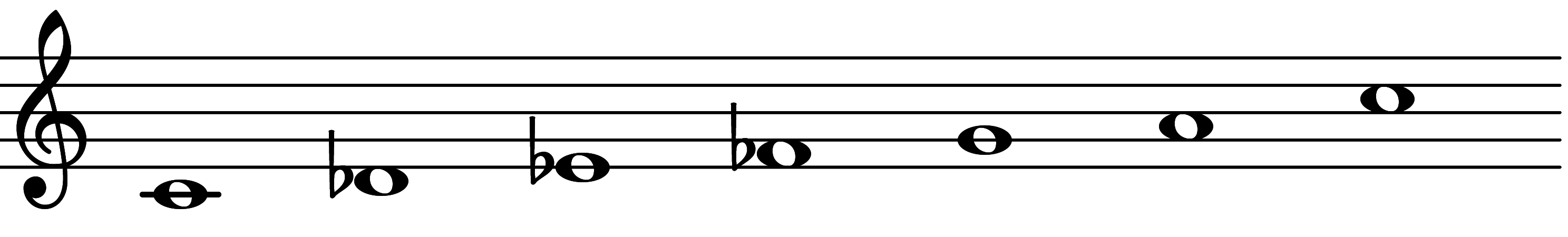 | Blues Dorian Hexatonic | ||
| Scale 699 | 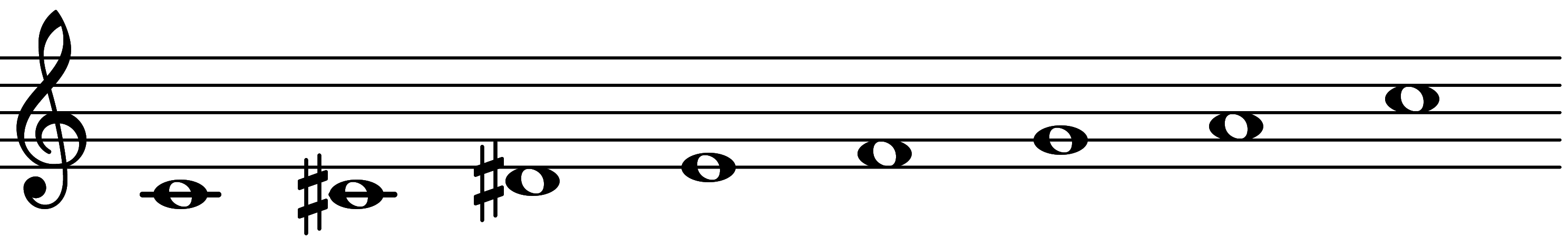 | Ultralocrian 5 | ||
| Scale 603 | 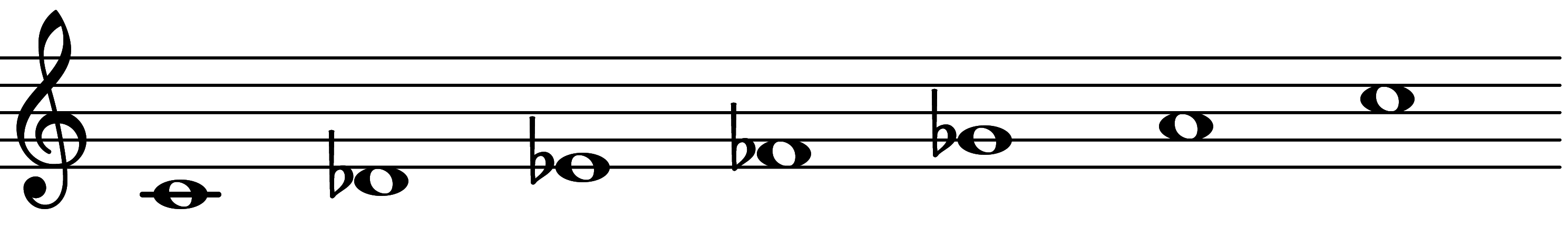 | 1◦ & 6MA | ||
| Scale 859 | 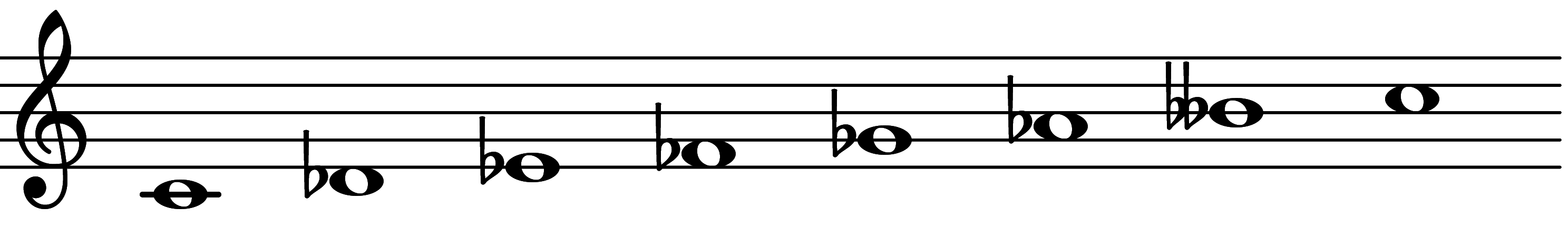 | Ultralocrian | ||
| Scale 987 |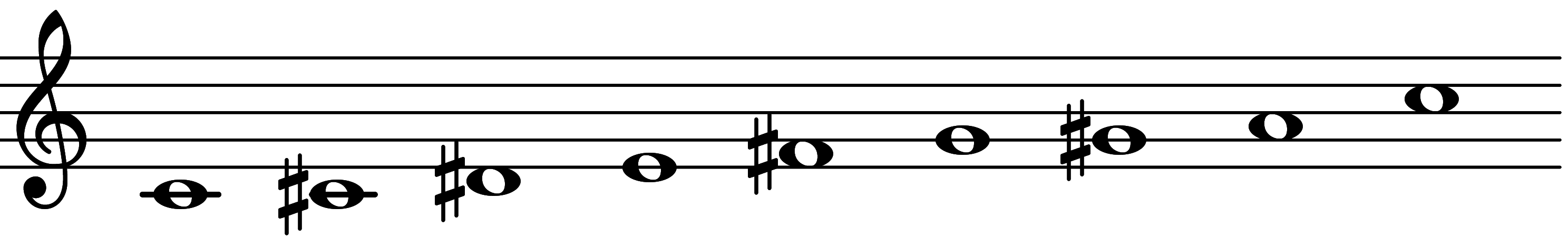  | 67 & 67 | ||
| Scale 219 | 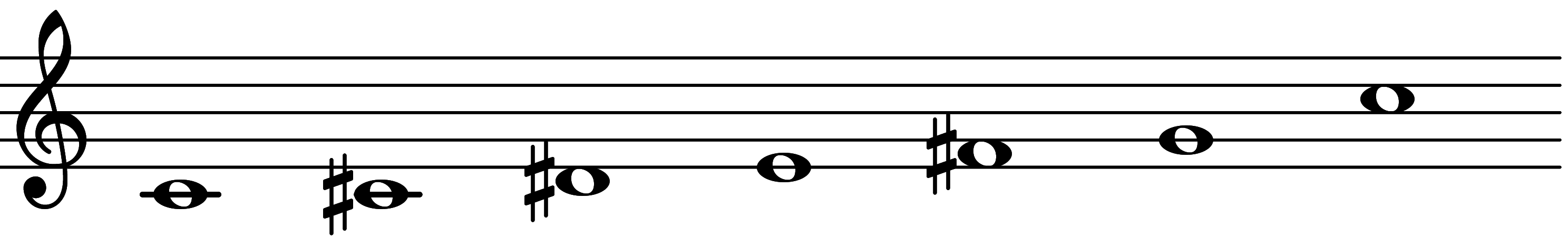 | Istrian | ||
| Scale 475 | 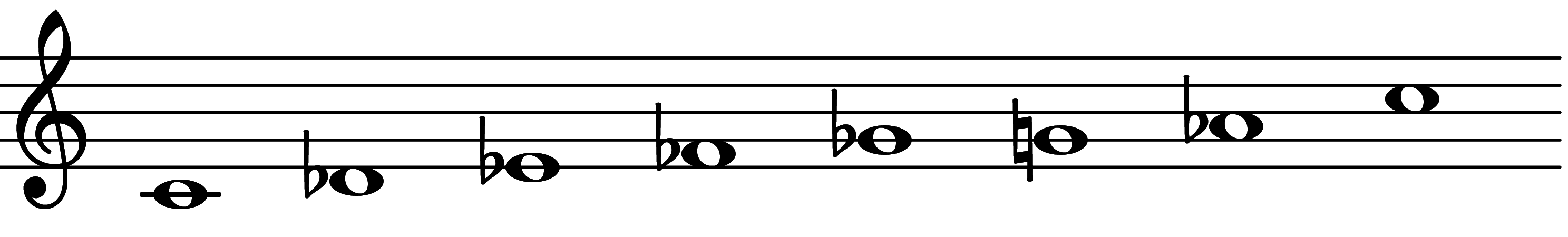 | Alt 67 | ||
| Scale 1243 |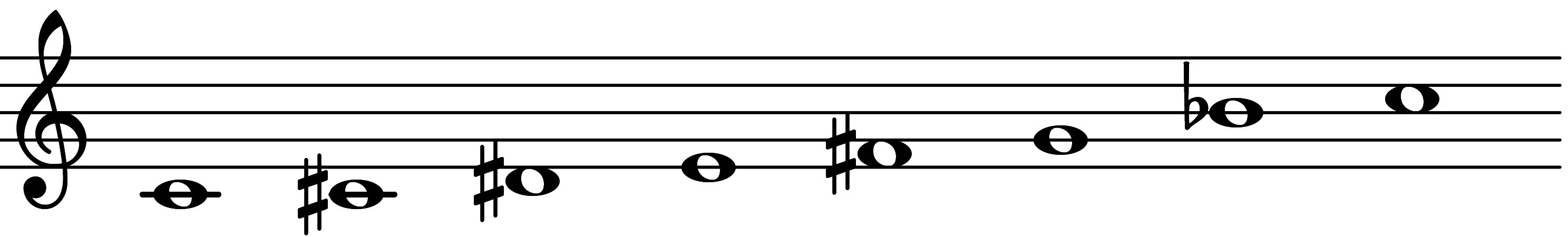  | Alt 6 | ||
| Scale 1755 |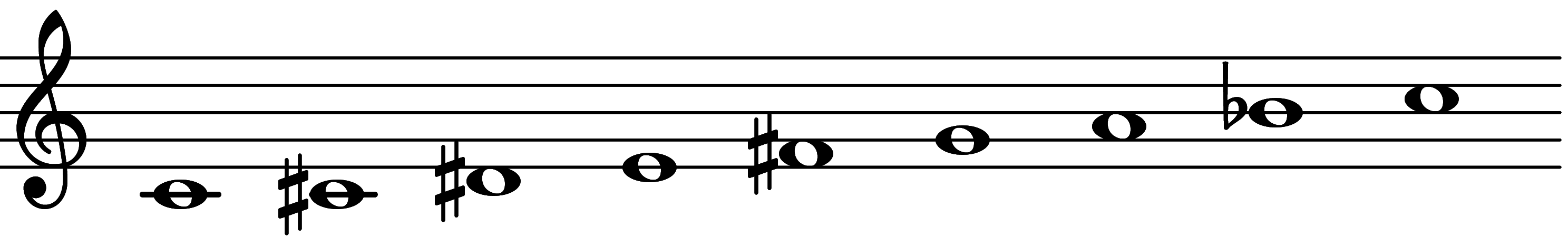  | Octatonic | ||
| Scale 2779 |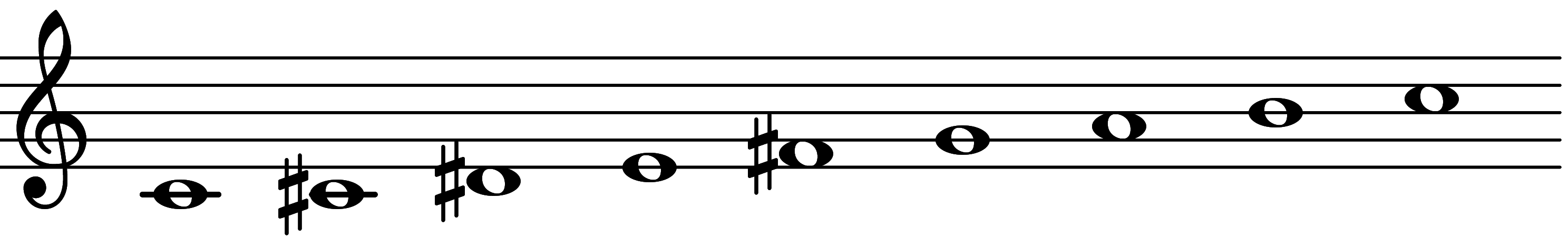  | Shostakovich |
This scale analysis was created by Ian Ring, Canadian Composer of works for Piano, and total music theory nerd. Scale notation generated by Lilypond, graph visualization by Graphviz, audio by TiMIDIty and FFMPEG. All other diagrams and visualizations are © Ian Ring. Some scale names used on this and other pages were invented by living persons, and used here with permission where required: notably collections of names by William Zeitler, Justin Pecot, Rich Cochrane, and Robert Bedwell.
Pitch spelling algorithm employed here is adapted from a method by Uzay Bora, Baris Tekin Tezel, and Alper Vahaplar. (DOI, Patent owner: Dokuz Eylül University, Used with Permission.
Tons of background resources contributed to the production of this summary; for a list of these peruse this Bibliography. Special thanks to Richard Repp for helping with technical accuracy, and George Howlett for assistance with naming the Carnatic ragas. Thanks to Niels Verosky for collaborating on the Hierarchizability diagrams. Gratitudes to Qid Love for the Xenomes. Thanks to B P Leonard for the Brightness metrics. Thanks to u/howaboot for inventing the Center of Gravity metrics.